Schools and universities are adopting AI-powered tools faster than ever, from adaptive learning platforms to predictive analytics. Without any concerns, artificial intelligence is changing how institutions work. But this rapid growth leaves many education leaders with the same question: What are the pros and cons of AI in education?
The benefits are clear: more personalized learning, less administrative burden, more accessibility. The risks are just as real: privacy concerns, high costs, fears of overreliance on machines. For school and university decision-makers, the question isn’t whether AI will impact education, but how to use it responsibly.
Based on our experience developing AI solutions for education, AnyforSoft has seen firsthand how AI can transform classrooms when applied properly. But we’ve also learned that successful adoption requires solutions aligned with institutional goals.
This article will guide you through:
- What does artificial intelligence in education really mean today.
- The main benefits of AI in education, with examples.
- The main drawbacks of AI in education, from bias to academic misconduct.
- Real-world use cases for K–12 and higher education.
- Practical advice to guide your decision.
By the end, you’ll know everything about the pros and cons of using AI in education. If you still can’t decide whether to implement AI in your educational processes after reading this article, take advantage of our expert consultation.
➡️For a broader look at how artificial intelligence is shaping the industry, explore our guide on AI in EdTech.
What Is Artificial Intelligence in Education?
Talking about the pros and cons of generative AI in education can feel abstract until you define what AI looks like in a classroom or university. Far from being a distant concept, artificial intelligence is already in tools that analyze student progress, personalize coursework, support teachers with daily tasks.
At its core, AI in education means using algorithms, machine learning and natural language processing to:
- Automate routine tasks like grading, scheduling and reporting.
- Analyze student data to uncover patterns and predict outcomes.
- Personalize coursework at scale, adapting to individual needs.
- Provide real-time support through AI tutors, chatbots and assistants.
- Improve accessibility through speech recognition, captioning and translation.
Examples in practice
AI in education is already changing how institutions work:
- Adaptive learning tools like DreamBox and Smart Sparrow adjust lessons in real time.
- AI writing assistants provide feedback during the drafting process.
- Learning management systems (LMS) have predictive dashboards to flag at-risk students.
AI in K–12 vs Higher Education
Applications vary by context:
- K–12: Focus on tutoring, reducing teacher workload, keeping students engaged.
- Higher education: Emphasis on predictive analytics for admissions, retention, scaling MOOCs.
Why this matters
The way schools and universities apply AI directly shapes how well it works. In K–12, it’s about keeping students engaged and giving teachers extra support. In higher education, it’s about data-driven insights, retention, and scaling learning for thousands of students.
Understanding this matters because it highlights a key point: AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Institutions need to adapt tools to their context – whether that means helping a middle school teacher manage a classroom of 30 or a university dean design strategies for thousands.
This sets the stage for evaluating the real pros and cons of AI in higher education and schools – advantages that can strengthen learning and challenges that need attention.
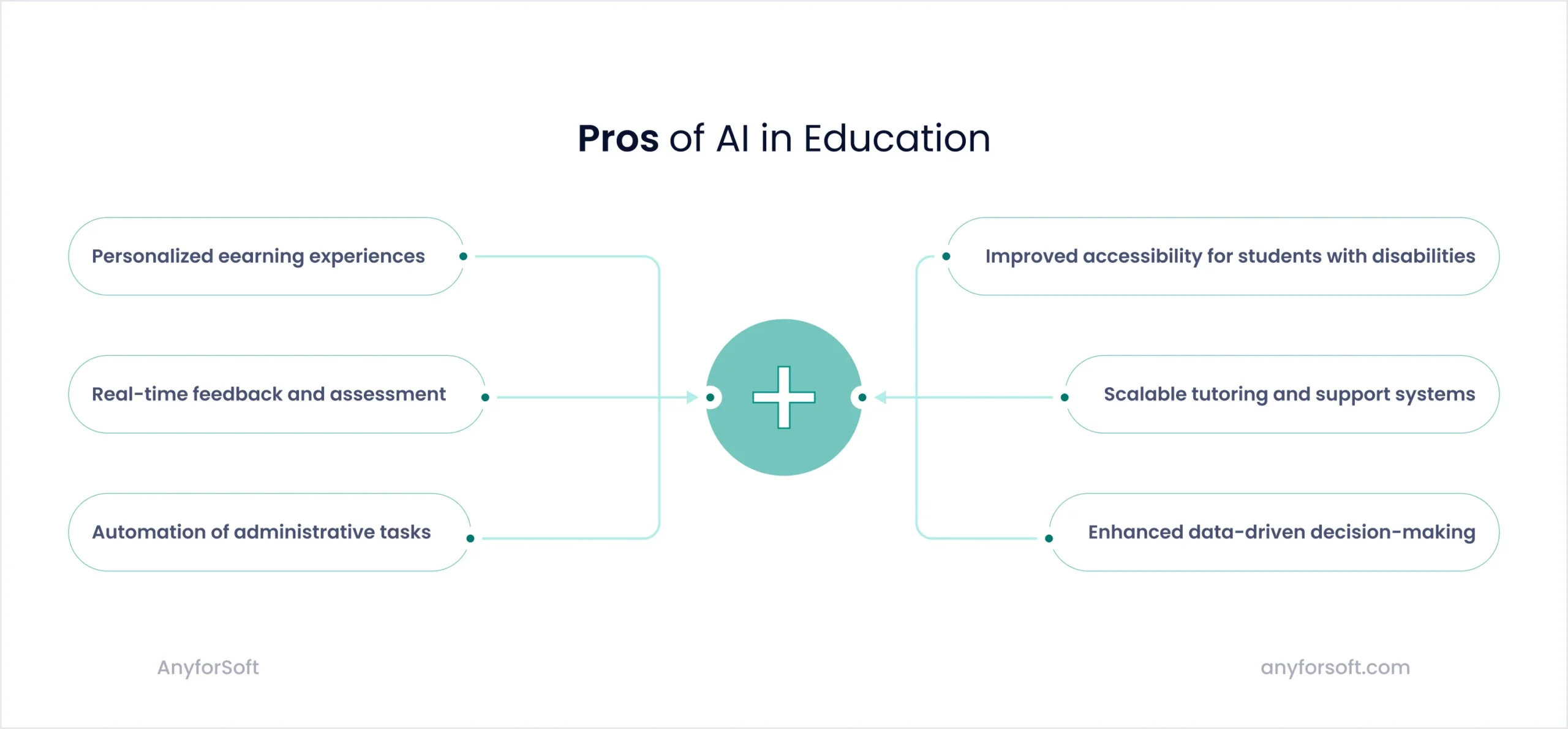
Pros of AI in Education
The benefits of AI in education are becoming more visible every year as schools, universities, and training providers experiment with new technologies. AI creates new opportunities to support student achievement – from tailoring learning journeys to freeing teachers from routine work.
1. Personalised learning experiences
Every learner progresses differently, yet classrooms often follow a single path. AI-powered platforms adapt to ability, pace, and learning style. Adaptive systems like DreamBox and Smart Sparrow fine-tune exercises in real time, keeping advanced learners challenged while supporting those who need reinforcement.
- Increases student engagement and retention.
- Supports inclusive learning pathways.
- Enables personalisation at scale without overwhelming teachers.
This kind of flexibility is why tailored learning is often cited as one of the top pros of AI in education.
2. Real-time feedback and assessment
Students used to wait days – or even weeks – for graded assignments. AI changes this. AI grading tools highlight mistakes as they happen, so learners can self-correct before issues snowball.
For educators, this means:
- Less time spent marking.
- More time available for mentoring.
- Better tracking of student progress.
3. Automation of administrative tasks
Repetitive tasks – attendance tracking, scheduling, compliance reports – take hours. AI can streamline these, giving faculty more time to teach and engage.
- Cuts down paperwork.
- Improves management efficiency.
- Reduces burnout.
4. Accessibility for students with disabilities
Accessibility is a core educational priority. AI supports this through voice recognition, text-to-speech, real-time captioning, and translation tools. These tools ensure learners with diverse needs are fully included in the experience.
5. Scalable tutoring and support systems
One-to-one tutoring is powerful, yet rarely scalable. AI tutors and chatbots change that, offering round-the-clock support.
Drawing on our experience building education platforms, adding AI-powered chat assistants has helped institutions scale student support without increasing staff costs.
➡️Find out how AI-driven chatbots for e-Learning can increase engagement and support students beyond the classroom.
6. Enhanced data-driven decision making
AI makes sense of vast performance data, uncovering patterns invisible to the human eye.
- Predicts student dropout risk.
- Guides curriculum changes.
- Informs resource allocation.
Cons of AI in Education
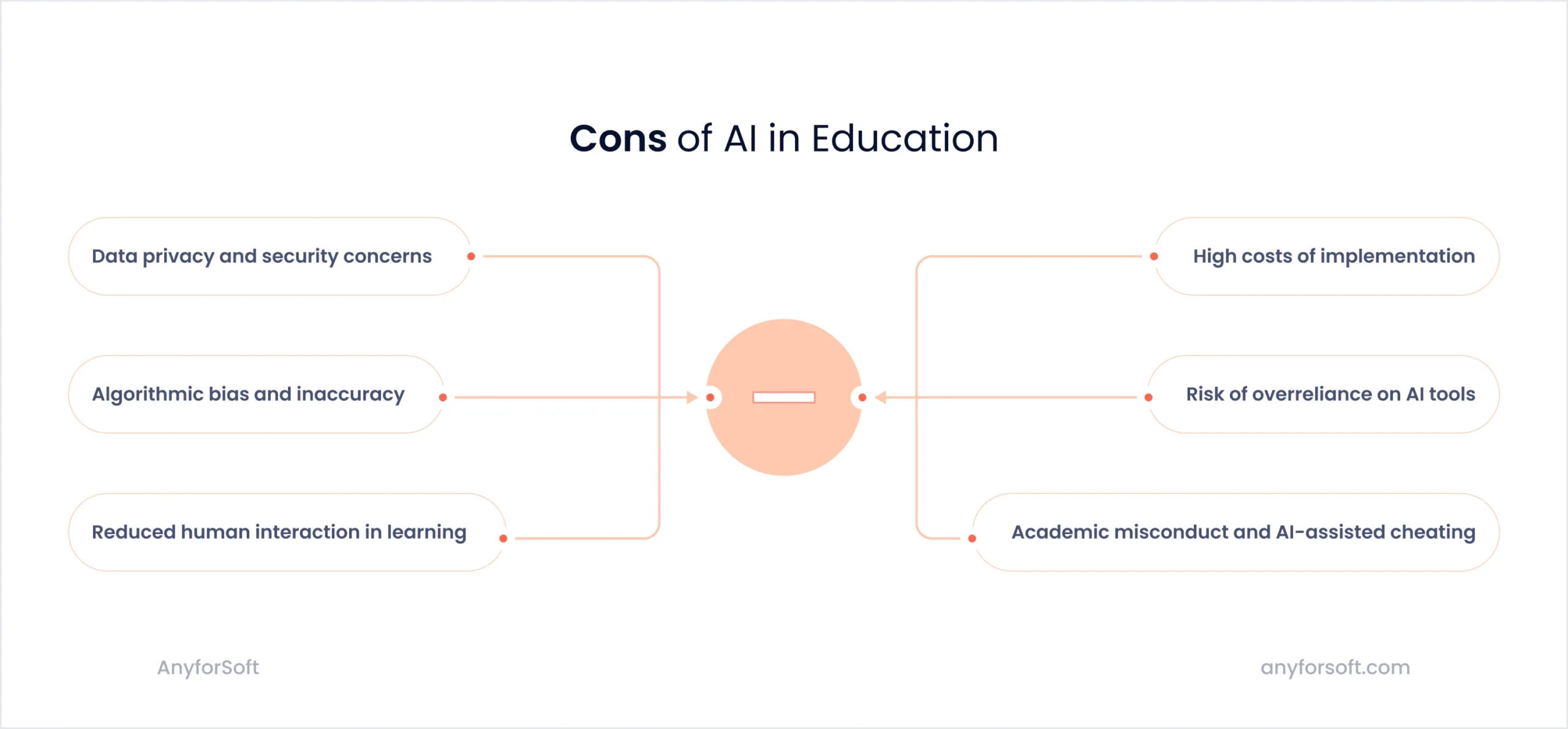
Yes, indeed, the benefits of artificial intelligence in education are quite impressive. Yet, thanks to our practical experience, we also know that there are several serious disadvantages of AI in education that we should keep in mind. Most of the concerns are around privacy, bias, cost, and the risk of losing human connection.
1. Data privacy and security concerns
AI systems need vast amounts of student data – grades, engagement metrics, even biometric inputs in some cases. This raises questions on how the data is stored, who has access, and if it can be misused.
- Compliance with FERPA, GDPR, and local laws is non-negotiable.
- Institutions must invest in secure systems.
- Parents, students, and faculty want to be assured of AI data privacy.
➡️ Explore best practices for managing AI data privacy to ensure compliance and protect student trust.
2. Algorithmic bias and inaccuracy
AI reflects the data it’s trained on. If data is biased, decisions on admissions or grading will unintentionally reinforce inequality.
3. Reduced human interaction in learning
AI can support but not replace human teachers with their mentorship and empathy. Over-automation will weaken social and emotional learning.
4. High cost of implementation
AI systems require infrastructure, licenses, and training. Smaller programs and certificate courses will struggle to justify the cost, especially in underfunded institutions.
5. Risk of overreliance on AI tools
Generative AI raises questions about critical thinking. If students overuse AI, they risk replacing deep analysis with shortcuts.
This is especially relevant when considering the pros and cons of generative AI in education, as generative tools provide outputs without fostering deep understanding.
6. Academic misconduct and AI-assisted cheating
AI-powered tools make it easier to bypass original work. Detection tools exist, but institutions must shape policies that encourage responsible use.
Real-World Examples of AI in Education
Theory only goes so far. To evaluate the pros and cons of using AI in education, you need to see how schools and universities are putting it into practice today. Our findings indicate that real-world case studies highlight both the promise and pitfalls of adoption.
Here are three areas where AI is already making a measurable impact:
AI tutors and virtual teaching assistants
Think back to your time in school or university. Have you ever found yourself working on a difficult assignment in the middle of the night and needing help from your teacher or quick answers more than ever? Well, this is exactly what AI tutors and virtual assistants are starting to offer.
- Duolingo’s AI Tutor: Uses natural language processing to simulate conversations in foreign languages, gives instant corrections.
- Stanford’s “Jill Watson” AI TA: Experimentally deployed in online forums, answers thousands of student questions and reduces faculty workload.
- AI Chatbots in Schools: Based on our experience building education platforms, chatbots integrated with a program’s CRM or LMS can:
- Answer student FAQs (deadlines, assignments, grades).
- Remind students about certificate or degree requirements.
- Reduce staff administrative burden while improving student satisfaction.
These assistants are not about replacing teachers, but expanding their reach. Thanks to our practical knowledge working with learning systems, we’ve seen how a chatbot can increase engagement on program pages and retention.
Adaptive learning platforms
Adaptive platforms show the artificial intelligence in education pros while also expose the limitations. They personalize coursework, track performance and adjust complexity dynamically.
Examples:
- Khan Academy’s Khanmigo (powered by GPT-4): Acts as a tutor, coach and writing assistant for millions of learners.
- DreamBox Learning: Provides math and reading pathways that adapt in real time to student answers.
- Coursera & edX: Universities use adaptive AI to tailor massive open online courses (MOOCs) to diverse learners.
Key benefits:
- Self-paced learning.
- Flags learning gaps early.
- Keeps students motivated through personalized challenges.
Key drawbacks:
- Requires massive data input (raises FERPA and consent issues).
- May overgeneralize learner performance, especially if algorithms misinterpret pauses, errors or engagement levels.
Our research has shown that adaptive platforms work best when combined with teacher oversight. Left unchecked, students can game the system or miss out on deeper understanding.
Predictive analytics in university admissions and retention
Universities are using AI-driven analytics to predict student success, improve retention and guide admissions decisions.
Real-world examples:
- Georgia State University: Uses predictive analytics to identify at-risk students, increases graduation rates by more than 20%.
- Arizona State University: Uses AI to optimize enrollment management and resource allocation.
- Public institutions in Europe: Have AI dashboards that alert faculty when engagement drops so they can intervene early.
Key applications:
- Lead-scoring: Ranking student applicants based on likelihood of success (not decision-making).
- Retention nudges: Automated reminders and personalized study suggestions.
- Business and administration programs: Using analytics to forecast which courses will have higher dropout rates.
Watch out for:
- Algorithmic bias: If training data is skewed towards historically successful groups, underrepresented students will be unfairly flagged.
- Lack of transparency: Many universities struggle to explain how AI made a decision — faculty and students don’t trust it.
From what we’ve seen, predictive analytics works best as decision support not a replacement for human judgment.
➡️Learn how to build an effective AI implementation strategy that balances innovation with ethics.
Conclusion
The pros and cons of AI in education show us that balance is key. AI personalizes learning, scales support, and empowers administrators with better insights. But it also raises questions of fairness, privacy, long-term impact, and cost.
Our findings show that institutions succeed when:
- Use AI as a partner to educators, not a replacement.
- Have clear policies for ethics and data use.
- Train faculty and students to use AI responsibly.
Based on our observations, careful planning allows schools and universities to get the benefits of AI in education while addressing the risks.
With our expertise in custom education software development, AnyforSoft helps schools and universities design platforms that balance innovation with trust. Contact us to get solution tailored to your goals.
FAQs
Is AI used differently in K–12 vs higher education?
Yes. K–12 is about tutoring and classroom support. Higher education is about analytics, retention, and MOOCs.
How does AI improve personalized learning?
By analyzing data in real time and adapting lessons to student needs – one of the biggest pros of AI in education.
What student data do AI tools collect?
Grades, engagement levels, participation metrics, and sometimes biometric information. Responsible management is key.
How much does it cost to implement AI-based systems in education?
- Small programs will spend thousands a year on lightweight tools.
- Universities and public institutions will invest six figures in enterprise platforms.
Will AI be in every classroom?
Most likely yes. Adoption will be gradual and driven by policies, funding, and faculty readiness.
